Understanding the Endocannabinoid System: Functions and Role in the Body
The human body is a complex network of interconnected systems, each working tirelessly to maintain balance, health, and overall well-being. Among these, one of the most fascinating and lesser-known is the endocannabinoid system (ECS). Although only discovered in the 1990s, the ECS plays a pivotal role in regulating various physiological processes. Its functions range from mood and sleep regulation to pain management and immune response.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive deep into what the endocannabinoid system is, how it functions, and why it has become such a vital focus of modern scientific research. We’ll also explore how CBD (cannabidiol) interacts with the ECS and why this interaction holds promise for natural wellness solutions.
What Is the Endocannabinoid System?
The endocannabinoid system is a biological regulatory system found in all vertebrates, including humans. Its primary role is to maintain homeostasis, which means keeping internal conditions stable and balanced despite external changes. Think of it as the body’s master regulator, fine-tuning various functions such as temperature, mood, energy levels, and even immune system activity.
Discovery of the ECS
The ECS was first identified in the late 20th century when researchers were studying how cannabis compounds, specifically THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), affected the human body. They discovered that the body naturally produces cannabinoid-like molecules, known as endocannabinoids. These molecules interact with a network of specialized receptors, forming what we now call the endocannabinoid system.
This groundbreaking discovery revolutionized our understanding of health and opened the door for new therapeutic possibilities involving plant-derived cannabinoids like CBD.
The Three Core Components of the ECS
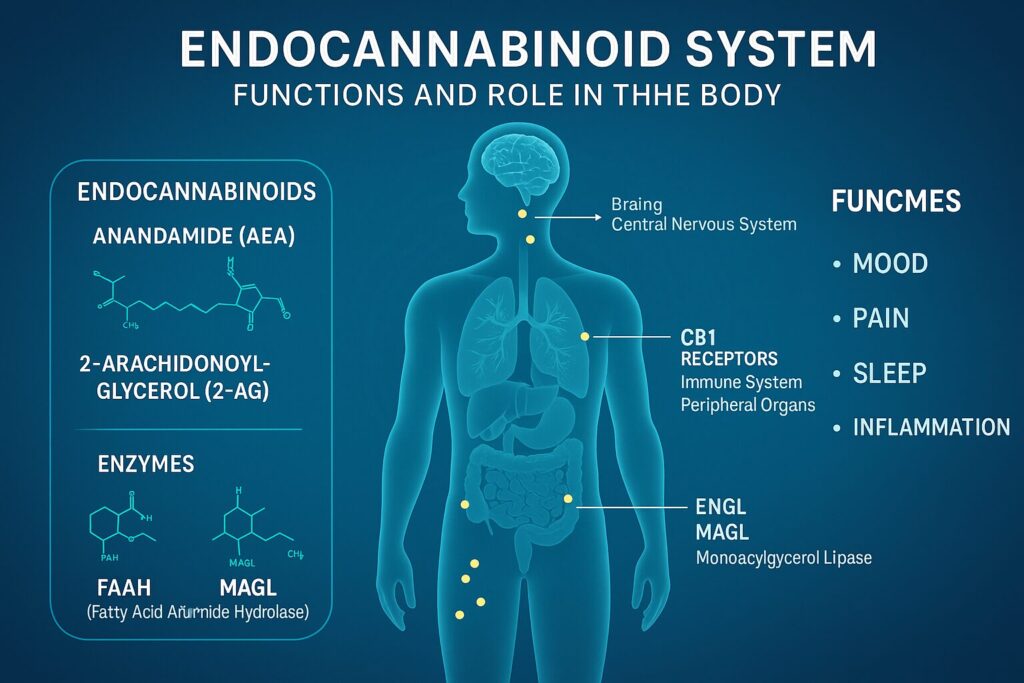
The ECS is made up of three primary components: endocannabinoids, receptors, and enzymes. Together, they form a dynamic system that helps regulate countless bodily processes.
1. Endocannabinoids
Endocannabinoids are naturally occurring compounds in the body that act similarly to cannabinoids found in cannabis plants. The two most well-studied endocannabinoids are:
-
Anandamide (AEA): Often called the “bliss molecule,” anandamide plays a key role in mood regulation and feelings of happiness or euphoria.
-
2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG): Primarily involved in immune system regulation and pain perception.
These molecules are produced on demand, meaning the body creates them only when needed to address imbalances.
2. Endocannabinoid Receptors
Receptors are the “communication hubs” of the ECS, receiving signals from endocannabinoids and triggering specific responses in the body. There are two main types:
-
CB1 Receptors: Found primarily in the brain and central nervous system. These receptors influence mood, memory, appetite, and coordination.
-
CB2 Receptors: Found in the immune system and peripheral organs. They play a vital role in managing inflammation and immune responses.
3. Enzymes
Once endocannabinoids have done their job, enzymes break them down to prevent overactivity. The two main enzymes are:
-
FAAH (Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase): Breaks down anandamide.
-
MAGL (Monoacylglycerol Lipase): Breaks down 2-AG.
This breakdown process ensures the ECS remains balanced and doesn’t overreact to stimuli.
Functions of the Endocannabinoid System
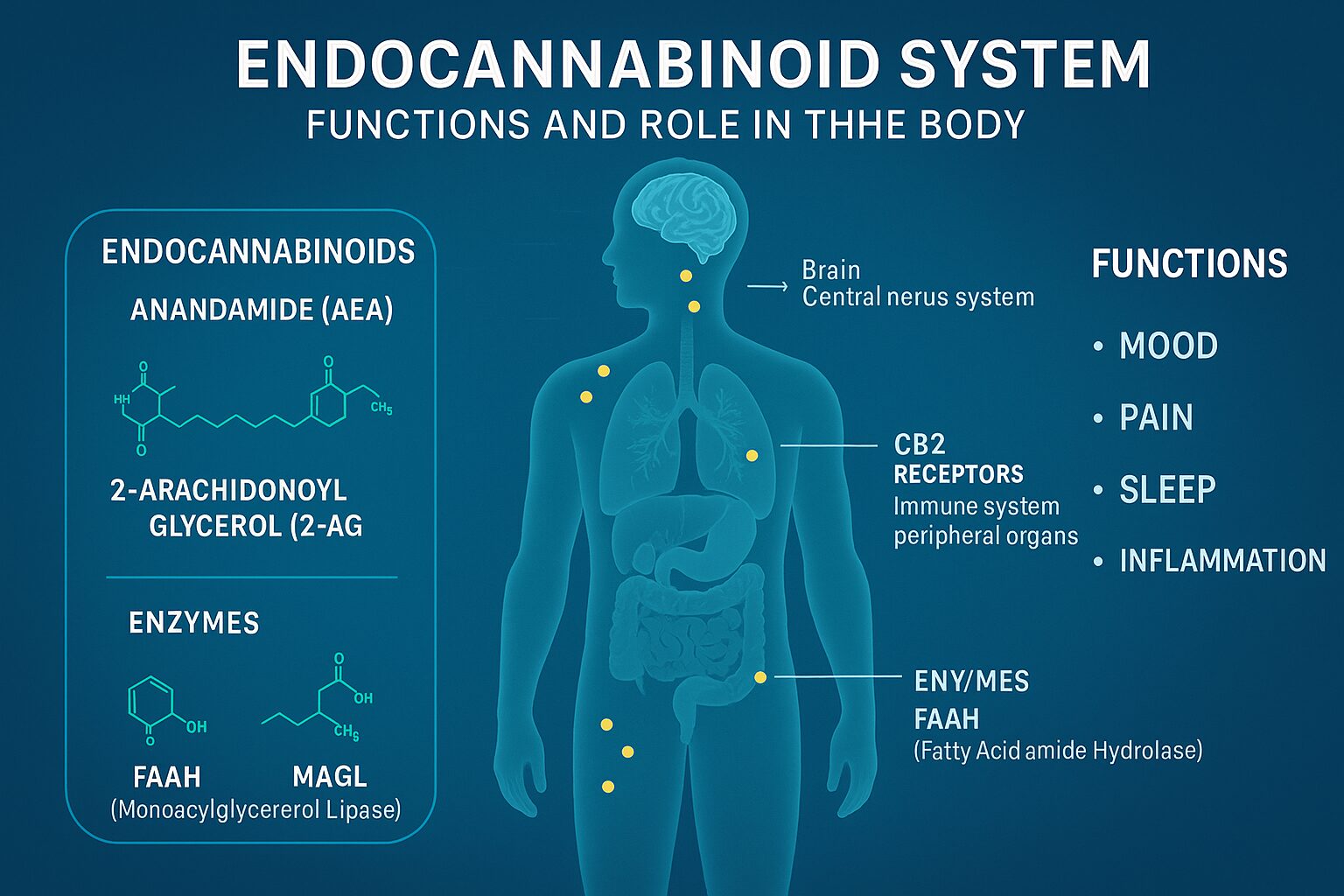
The ECS is incredibly versatile, influencing almost every major system in the body. Below are some of its most critical functions:
1. Mood Regulation
The ECS has a direct impact on emotional well-being. By interacting with CB1 receptors in the brain, endocannabinoids help regulate neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which are linked to happiness, stress relief, and emotional stability.
2. Pain and Inflammation Management
CB2 receptors are crucial in managing the body’s inflammatory response. When activated, they help reduce swelling, pain, and tissue damage, making the ECS a natural target for pain relief therapies.
3. Sleep Cycle Regulation
The ECS influences circadian rhythms, which govern our sleep-wake cycles. Proper ECS function is essential for falling asleep, staying asleep, and achieving restorative sleep.
4. Immune System Modulation
The ECS plays a dual role in the immune system by stimulating responses when needed and calming them when they become overactive, helping to prevent chronic inflammation and autoimmune issues.
5. Appetite and Metabolism
CB1 receptors in the hypothalamus are involved in hunger regulation. This is why cannabis is often associated with increased appetite, commonly known as “the munchies.”
The ECS and Homeostasis: Keeping the Body in Balance
Homeostasis is the body’s way of staying balanced despite external changes. The ECS acts as a feedback loop, constantly monitoring systems and making adjustments as needed.
For instance:
-
When body temperature rises, the ECS signals mechanisms to cool it down.
-
When stress hormones spike, the ECS works to restore calm.
Without a properly functioning ECS, the body is more prone to disease, inflammation, and dysfunction.
The Role of CBD in Supporting the ECS
CBD (cannabidiol) is a non-psychoactive compound derived from hemp and cannabis plants. Unlike THC, it doesn’t cause a “high.” Instead, CBD interacts with the ECS in subtle yet powerful ways.
How CBD Interacts with the ECS
CBD doesn’t bind directly to CB1 or CB2 receptors like THC does. Instead, it influences the system by:
-
Enhancing Endocannabinoid Production: CBD helps the body produce more of its own natural cannabinoids.
-
Inhibiting Enzymes Like FAAH: This slows the breakdown of anandamide, allowing it to stay active longer.
-
Modulating Receptor Activity: CBD fine-tunes receptor sensitivity, promoting balance.
These actions collectively support the ECS in maintaining homeostasis and overall well-being.
Health Benefits of CBD Through ECS Support
By interacting with the ECS, CBD may provide a wide range of potential health benefits. While research is ongoing, studies and anecdotal reports suggest positive outcomes in the following areas:
1. Stress and Anxiety Relief
CBD’s influence on serotonin receptors can help reduce anxiety and improve mood, offering a natural alternative to pharmaceuticals.
2. Pain Management
Many users report relief from chronic pain conditions like arthritis, migraines, and muscle soreness due to CBD’s anti-inflammatory properties.
3. Improved Sleep Quality
CBD has been shown to help individuals fall asleep faster and stay asleep longer by regulating sleep cycles through ECS modulation.
4. Neuroprotection
Preliminary research suggests CBD may help protect brain cells and support cognitive function, making it a potential aid for neurodegenerative disorders.
5. Immune System Support
CBD’s ability to balance immune responses could play a role in reducing autoimmune symptoms and enhancing overall immunity.
Signs of an Imbalanced ECS
An underactive or overactive ECS can lead to various health issues. Some signs that your ECS may be out of balance include:
-
Chronic pain or inflammation
-
Sleep disturbances or insomnia
-
Anxiety or depression
-
Frequent illness or weakened immunity
-
Irregular appetite or digestion problems
CBD and other lifestyle changes, like diet and exercise, can help restore balance.
Supporting Your ECS Naturally
In addition to using CBD products, there are several ways to naturally support your ECS:
1. Diet
Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids (like salmon, walnuts, and flaxseeds) are essential for endocannabinoid production.
2. Exercise
Physical activity naturally boosts endocannabinoid levels, particularly anandamide.
3. Stress Reduction
Practices like meditation, yoga, and deep breathing support ECS health by lowering stress hormone levels.
4. Quality Sleep
Adequate, restorative sleep is critical for ECS function and overall wellness.
How to Choose the Right CBD Product
When incorporating CBD into your wellness routine, quality matters. Here’s what to look for:
-
Third-Party Lab Testing: Verify the product’s purity and potency.
-
Full-Spectrum CBD: Contains additional cannabinoids and terpenes for enhanced effects.
-
Organic Sourcing: Hemp should be grown without pesticides or harmful chemicals.
-
Proper Dosage Information: Clear guidelines for safe and effective use.
The Future of ECS Research
The discovery of the ECS is still relatively recent, and scientists are continually uncovering new insights. Future research may lead to advanced treatments for conditions like chronic pain, anxiety disorders, and neurodegenerative diseases. CBD and other plant-based cannabinoids are expected to play a central role in these developments.
Conclusion
The endocannabinoid system is one of the most vital yet underappreciated systems in the human body. By maintaining balance across various physiological processes, it helps keep us healthy and resilient. CBD, through its interaction with the ECS, offers a natural and promising way to support this balance.
As research continues, our understanding of the ECS and CBD’s role will only deepen, paving the way for innovative, natural wellness solutions. For those seeking to improve their well-being, CBD products can be a powerful tool when used mindfully and with quality in mind.
