Cannabidiol, commonly known as CBD, has taken the wellness world by storm. From oils and tinctures to capsules and topical creams, CBD products are now widely available and used by millions worldwide. But how does this natural compound actually work within the body to promote balance and well-being?
The answer lies in a fascinating and complex network called the endocannabinoid system (ECS). This system plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis — the body’s internal balance — and is directly influenced by cannabinoids like CBD. Understanding how CBD interacts with the ECS is key to unlocking its potential benefits for health and wellness.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the science behind CBD and its relationship with the ECS, how this interaction affects the body, and what the latest research says about CBD’s therapeutic potential.
The Basics: What is CBD?
CBD is a non-psychoactive compound found in hemp and cannabis plants. Unlike THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), the compound responsible for the “high” associated with marijuana, CBD does not produce intoxicating effects. Instead, it works subtly, helping to regulate various bodily functions by interacting with natural processes.
Over the past decade, CBD has become popular as a natural supplement for:
-
Stress relief and relaxation
-
Pain and inflammation management
-
Sleep improvement
-
Mood enhancement
-
General wellness support
But to truly understand how CBD achieves these effects, we need to examine the endocannabinoid system — the key network it interacts with.
Introduction to the Endocannabinoid System (ECS)
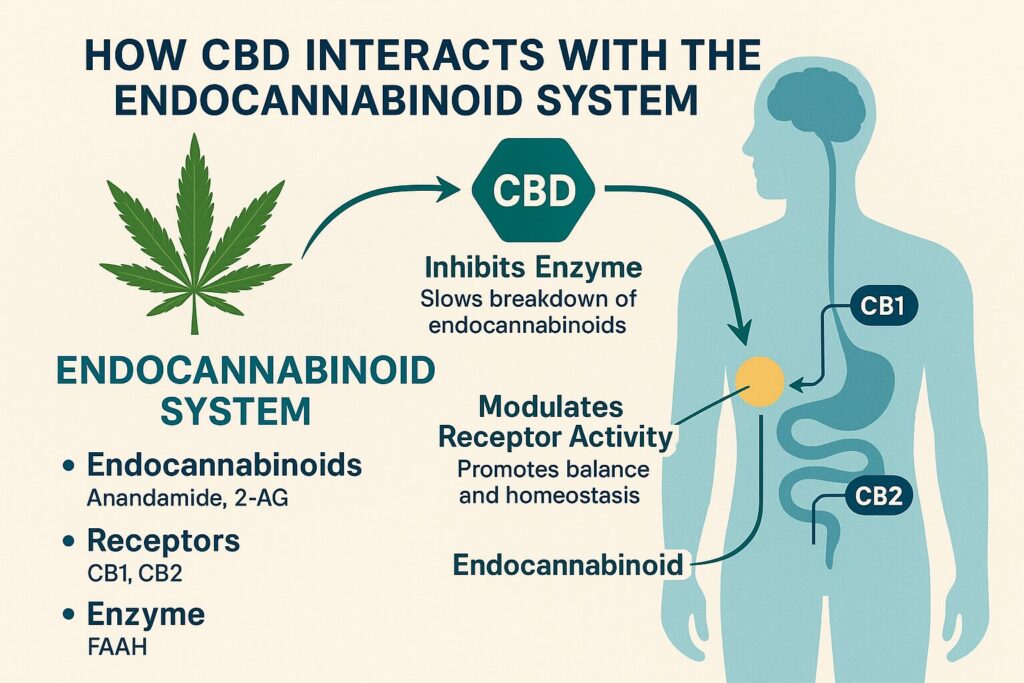
The ECS is a cell-signaling system present in all mammals. Discovered in the 1990s, it is composed of three main parts:
-
Endocannabinoids – Molecules produced naturally by the body.
-
Receptors – Located throughout the body to receive signals from cannabinoids.
-
Enzymes – Responsible for breaking down endocannabinoids once they’ve done their job.
The ECS helps regulate essential processes such as:
-
Mood
-
Sleep cycles
-
Appetite
-
Immune responses
-
Pain perception
-
Memory and cognitive function
Its primary goal is homeostasis, keeping everything balanced and functioning optimally.
Key Components of the ECS
1. Endocannabinoids
These are cannabinoid-like molecules naturally produced by the body. The two most well-researched endocannabinoids are:
-
Anandamide (AEA): Known as the “bliss molecule,” involved in mood and emotional well-being.
-
2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG): Plays a major role in immune function and pain regulation.
These molecules act as messengers, signaling the body when it needs to adjust certain functions.
2. Cannabinoid Receptors
Receptors are proteins found on cell surfaces. They receive signals from endocannabinoids and phytocannabinoids (like CBD and THC). There are two primary types:
-
CB1 Receptors: Concentrated in the brain and central nervous system. They influence mood, appetite, memory, and motor control.
-
CB2 Receptors: Found mostly in the immune system and peripheral organs, affecting inflammation and immune responses.
3. Enzymes
Enzymes break down endocannabinoids after they’ve completed their function. Two primary enzymes are:
-
FAAH (Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase): Breaks down anandamide.
-
MAGL (Monoacylglycerol Lipase): Breaks down 2-AG.
This ensures that the ECS operates smoothly without overstimulation.
How CBD Interacts with the ECS
Unlike THC, which directly binds to CB1 and CB2 receptors, CBD interacts indirectly. This unique mechanism explains why CBD does not cause psychoactive effects and why it’s often associated with gentle, balancing outcomes.
Here’s how CBD works within the ECS:
1. Inhibits Enzyme Activity
CBD prevents the enzyme FAAH from breaking down anandamide too quickly. This allows higher levels of anandamide to remain active in the body, which can improve mood, reduce anxiety, and enhance overall well-being.
Result: A natural boost in “feel-good” endocannabinoids.
2. Modulates Receptor Activity
CBD doesn’t directly activate receptors but instead modulates their activity, influencing how they respond to signals. This fine-tuning helps maintain balance without overwhelming the system.
3. Activates Non-Cannabinoid Receptors
Research shows that CBD also interacts with other receptors beyond the ECS, such as:
-
Serotonin Receptors (5-HT1A): Linked to mood stabilization and anxiety reduction.
-
TRPV1 Receptors: Involved in pain perception and inflammation.
This multi-faceted approach contributes to CBD’s broad range of potential health benefits.
The Balance Between CBD and THC
Both CBD and THC are cannabinoids, but they have very different effects on the body.
| Feature | CBD | THC |
|---|---|---|
| Psychoactive Effects | No | Yes (causes a “high”) |
| Binding to CB1/CB2 | Indirect | Direct |
| Primary Benefits | Balance, relaxation, wellness | Euphoria, pain relief |
| Legal Status (U.S.) | Federally legal if hemp-derived | Restricted in many states |
Interestingly, CBD can counteract some of THC’s effects, such as anxiety or paranoia, by modulating CB1 receptor activity.
Health Benefits of CBD Through ECS Interaction
Because the ECS influences so many bodily functions, CBD’s interaction with this system has wide-reaching implications for health and wellness.
1. Stress and Anxiety Reduction
By increasing anandamide levels and interacting with serotonin receptors, CBD may help:
-
Reduce stress responses
-
Improve resilience to daily challenges
-
Enhance overall mood
Many people report a sense of calm and relaxation after taking CBD.
2. Pain Relief
CBD’s interaction with CB2 receptors and TRPV1 receptors helps manage pain and inflammation. It’s especially promising for:
-
Arthritis and joint pain
-
Muscle soreness
-
Migraines
-
Neuropathic pain
3. Improved Sleep Quality
Poor sleep often stems from stress, pain, or hormonal imbalances. By addressing these underlying issues, CBD may help improve:
-
Sleep onset (falling asleep faster)
-
Sleep duration
-
Sleep quality
4. Support for Immune Health
CBD’s modulation of CB2 receptors helps regulate immune system activity, potentially aiding conditions related to inflammation or immune overactivity.
5. Neuroprotection
Preliminary studies suggest that CBD may protect brain cells and support neurological health, showing promise for disorders like epilepsy and multiple sclerosis.
Scientific Studies on CBD and the ECS
The scientific community is actively researching CBD and its interaction with the ECS. Here are a few key findings:
-
2018 Study on Anxiety: Found that CBD significantly reduced anxiety in individuals before public speaking.
-
2019 Review on Sleep Disorders: Suggested CBD may help improve sleep quality and reduce insomnia.
-
2020 Study on Pain Management: Highlighted CBD’s role in reducing chronic pain without the side effects of traditional medications.
While more research is needed, these studies provide a strong foundation for CBD’s therapeutic potential.
Factors That Influence CBD’s Effectiveness
CBD’s interaction with the ECS can vary depending on several factors:
1. Dosage
The right dosage varies from person to person. Too little may be ineffective, while too much could cause unwanted side effects like drowsiness.
2. Method of Consumption
How you take CBD affects how quickly it works and how long the effects last:
-
Tinctures and oils: Absorbed quickly under the tongue.
-
Capsules and edibles: Slower onset but longer-lasting effects.
-
Topicals: Target specific areas like joints or muscles.
3. Individual Biochemistry
Everyone’s ECS is slightly different. Factors like genetics, age, and lifestyle can influence how CBD interacts with your body.
4. Product Quality
High-quality, third-party-tested CBD products ensure purity and potency, maximizing potential benefits.
Tips for Supporting Your ECS Naturally
CBD is a powerful tool, but you can also support your ECS through natural lifestyle choices:
1. Diet
Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids support endocannabinoid production. Include foods like:
-
Salmon
-
Walnuts
-
Flaxseeds
-
Chia seeds
2. Exercise
Physical activity boosts anandamide levels, helping the ECS function optimally. Even light activities like walking or yoga are beneficial.
3. Stress Management
Chronic stress can disrupt the ECS. Practices like meditation, deep breathing, and mindfulness help maintain balance.
4. Sleep Hygiene
Quality sleep is essential for ECS regulation. Aim for 7-9 hours of restful sleep per night.
Choosing the Right CBD Product
To maximize CBD’s interaction with your ECS, select products carefully:
-
Full-Spectrum CBD: Contains multiple cannabinoids and terpenes for the “entourage effect.”
-
Third-Party Testing: Verify purity and potency through lab reports.
-
Proper Dosage Guidance: Clear instructions for safe and effective use.
-
Organic Sourcing: Hemp should be grown without harmful chemicals or pesticides.
The Future of CBD and ECS Research
The field of cannabinoid science is rapidly evolving. As research continues, we can expect to uncover:
-
New therapeutic uses for CBD
-
Deeper understanding of ECS mechanisms
-
Innovative products tailored for specific health needs
CBD’s potential is vast, and its role in natural wellness will likely grow in the coming years.
Conclusion
CBD’s interaction with the endocannabinoid system represents a natural and holistic way to support health and well-being. By modulating receptors, enhancing endocannabinoid levels, and influencing other pathways, CBD helps the body maintain balance and resilience.
For those seeking a plant-based approach to wellness, CBD offers a promising option. As always, consult with a healthcare provider before beginning any new supplement regimen, and choose high-quality products to ensure safety and effectiveness.
